基本原则
- mysql书写顺序和执行顺序都是按照
select-from-where-group by-having-order by-limit进行的 - MySQL中子结果集必须使用别名,而Oracle中不需要特意加别名
不同数据库差异
- 可使用ETL工具kettle对不同数据库中的数据做迁移和同步
- Oracle迁移MySQL注意事项
- Oracle 11g表名最大长度为30,Mysql最大长度为64
数据类型转换
- mysql:
cast()和convert()可将一个类型转成另外一个类型- 语法:cast(expr as type)、convert(expr, type)、convert(expr using transcoding_name)
1 | -- mysql、h2。可用类型:二进制 BINARY、字符型,可带参数 CHAR()、日期 DATE、TIME、DATETIME、浮点数 DECIMAL、整数 SIGNED、无符号整数 UNSIGNED |
日期
- 日期数据类型转换见上文: 数据类型转换参考
1 | -- mysql |
时区相关
- 参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/scoopr/p/5592339.html
- Oracle和MySQL中的timestamp的作用是不同的
- Oracle中,TIMESTAMP是对date的更高精度的一种存储,是作为datetime的延展,但它不存储时区信息(Date不含微妙级时间)
- Oracle中,TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE存储时区信息
- Oracle中,TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE不会存储时区信息,会将传入时间数据转换为数据库时区的时间数据进行存储,但不存储时区信息;客户端检索时,oracle会将数据库中存储的时间数据转换为客户端session时区的时间数据后返回给客户端
- MYSQL中,TIMESTAMP是为了更少的存储单元(DATETIME为4字节,TIMESTAMP为1个字节)但是范围为1970的某时的开始到2037年,而且会根据客户端的时区判断返回值,MYSQL的TIMESTAMP时区敏感这点和ORACLE的TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE一致
- ORACLE和MYSQL的函数返回不一样
- oracle读取的时区信息是以client端为准,CURRENT_TIMESTAMP都受到客户端SESSION TIMEZONE影响,而SYSDATE,SYSTIMESTAP不受影响
- mysql读取的时区信息是以server端为准,NOW(),SYSDATE(),CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 均不受到客户端连接时区影响
- Oracle的DBTIMEZONE只和TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE有关。MySQL中的time_zone直接影响所有的timestamp取值
- 为了返回一致的数据MYSQL设置TIME_ZONE参数即可,因为他是每个连接都会用到的;但是ORACLE最好使用SYSDATE或者SYSTIMESTAMP来直接取DB SERVER端时间
- MySQL修改时区信息,只要CLIENT端的时区信息不变,此无影响
- Oracle修改时区信息,同理,TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE不受影响,TIMESTAMP和TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE会发生变化
- 如果在client中不指定时区信息,oracle以client端的时区信息为准,要进行转换,mysql以server端的时区信息为准
1 | -- oracle |
其他
- 查询空白表
1 | -- mysql |
- 查询前几条
1 | -- mysql |
- 关键字转义
1 | select * from `user`; -- mysql |
- 空值
1 | -- oracle: null包含了空字符串('' == null) |
- 空值排序
1 | order by my_field [asc|desc] nulls [first|last] -- oracle |
- 中文排序
1 | -- mysql |
- 字符串类型值
1 | -- Mysql 可以使用单引号或双引号,Oracle只能使用单引号 |
- as用法
1 | -- Mysql/Oracle两种写均支持。只不过mybatis操作oracle返回map时,第一种写法的key全部为大写,第二种写法的key为小写 |
- 多字段查询
1 | -- oracle |
- 数值比较
1 | -- 假设两个字段一个是number(10, 2)的, 一个是FLOAT的则比较可能会有问题,可进行cast/round转换再比较 |
- (oracle)decode替代
1 | -- oracle |
- uuid
1 | -- sqlserver 32位 |
读锁问题
- A事物(基于ID)更新表test暂未提交,此时B事物读取test表
- Mysql: B事物可正常执行读取
- SqlServer: B事物会阻塞,直到A事物提交或回滚释放锁(A事物持有test的IX锁,B事物持有IS锁). 多线程可能存在问题
- SqlServer(多线程)死锁案例
- SQL Server 默认隔离级别为 READ COMMITTED,子线程读取时需等待主线程事务提交
- 解决方案
- 移除异步逻辑,同步执行
- 若必须异步,使用无事务的独立服务
- 使用 Spring @Async 注解(使用新的事物): 参考spring.md#多线程@EnableAsync
- 利用事务同步管理器(精细控制): TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization
1 | // 下面的伪代码会导致 SqlServer 项目卡死 => 进而可能连接池升高 |
复制表数据
- 复制表结构参考
- create table … as select
- 复制表数据
- insert into … select
更新数据
1 | -- mysql |
关联表进行数据更新
update set from where将一张表的数据同步到另外一张表
1 | -- Oracle:如果a表和b表的字段相同,最好给两张表加别名. **注意where条件**,idea可能出警告 |
- 实例
1 | -- (1) |
merge into同步表
- 场景
- 数据同步:将临时表或外部数据源同步至主表
- 批量初始化:避免重复插入已有数据,仅更新或补充新记录
1 | -- 语法 |
更新前几行数据
1 | -- oracle: 优先更新某个字段完全匹配的数据,没有完全匹配则更新该字段为空的数据 |
不查询某个字段(获取列信息)
1 | -- mysql |
环境变量和自定义变量
- oracle案例: 记录数据变动日志
- oracle: https://blog.csdn.net/db_murphy/article/details/115186884
- mysql: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36528734/article/details/81187863
复杂查询
- count是统计该字段不为空的行数,可结合distinct使用,如
count(distinct case when u.sex = '1' then u.city else null end )
基于用户属性表统计每个公司不同用户属性的用户数
1 | -- 1个公司对应多个用户,1个用户对应多个属性 |
基于关系表统计多个关系同时存在的主表记录
1 | /* |
基于主子孙表求和统计
1 | select count(1) "艘次", sum(a.net_ton) "总净吨", sum(a.gweight_ton) "代理货物总量(万吨)", sum(a.bc_count) "代理集装箱量" |
行转列/列转行
1 | /* |
oracle
使⽤ decode 与聚合函数实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7select t.name,
sum(decode(t.course,'chinese', score, null)) as CHINESE,
sum(decode(t.course,'math', score, null)) as MATH,
sum(decode(t.course,'english', score, null)) as ENGLISH
from students t
group by t.name
order by t.name使⽤ case when 与聚合函数实现,类似decode
使⽤ pivot 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16select * from
select name, chhinese, math, english from students
pivot(
max(score) -- max ⾥是要转的列的值
for course -- 需要转的列名称
in('chinese' chhinese, 'math' math, 'english' english)
)
order by name;
-- 扩展说明: pivot的xml字句
-- bill_fee_cod_xml为xmltype格式(mybatis无法解析), getstringval为转成XML字符串(但是最大长度时4000), getclobval为转成clob格式(内容还是xml)
select ship_no, bill_nbr, bill_fee_cod_xml, (bill_fee_cod_xml).getstringval(), (bill_fee_cod_xml).getclobval()
from bill_fee
-- 以 XML 格式显示 pivot 操作的输出,在plsql中显示成了xmltype;此时对应字段为bill_fee_cod的后面加上_xml
pivot xml (sum(MONEY_NUM) for bill_fee_cod in(select BILL_FEE_COD from bill_fee where port_id = '1' and trust_cod = 'CUL'))
where port_id = '1' and trust_cod = 'CUL'动态行转列(列名不固定)
- 基于存储过程动态拼接SQL,参考sql-procedure.md#sql_pivot_dynamic_col动态行转列
- 基于存储过程动态拼接SQL和视图 https://blog.csdn.net/Huay_Li/article/details/82924443
- 查询每次新增临时查询ID和时间,再定时删掉老的数据;第一次查询创建几百个字段的视图(无实际意义的字段名),并把列头以一行值的形式显示到结果中(第一行值充当列头)
- 合并到一个字段
- 参考Oracle wm_concat行转列
- SqlServer的 STRING_AGG, 用法一致
- 参考Oracle listagg within group行转列, 类似wm_concat
- 参考Oracle wm_concat行转列
mysql
1 | -- 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/7151433.html |
sqlserver
- 行转列:
PIVOT用于将列值旋转为列名;也可用聚合函数配合CASE语句实现 - 列转行:
UNPIVOT用于将列明转为列值;也可以用UNION来实现
1 | -- ## 行转列 |
逗号分割数据翻译
- sqlserver
1 | -- 2016以上 |
拆分以逗号分隔的字符串为多行
- oracle参考下文正则表达式 regexp_substr
SQL语句记录
1 | -- 查询和id=1性别一样的用户. 通过一条记录关联后过滤其他数据 |
Mysql
常见问题
- 查询空格问题。如:
select * from test t where t.name = 'ABC';和select * from test t where t.name = 'ABC ';(后面有空格)结果一致,ABC和ABC都可以查询到数据库中ABC的数据,区分方法- 使用like:
select * from test t where t.name like 'ABC';(不要加%,使用mybatis-plus插件可开启字符串like查询) - 使用关键字 binary:
select * from test t where t.name = binary'ABC'; - 使用length:
select * from test t where t.name = 'ABC' and length(t.name) = length('ABC');
- 使用like:
- 字段值不区分大小写问题(oracle默认区分大小写, sqlserver默认不区分大小写)
- 如果字段为
utf8_general_ci存储时,可以在字段前加binary强行要求此字段进行二进制查询,即区分大小写。如select * fromt_testwhere binary username = 'aezocn' - 设置字段排序规则为
utf8_bin/utf8mb4_bin(utf8_general_ci中ci表示case insensitive,即不区分大小写)。设置成utf8_bin只是说字段值中每一个字符用二进制数据存储,区分大小写,显示和查询并不是二进制。设置成bin之后select * from user t where name = 'Test';区分大小写 - utf8mb4_unicode_ci 和 utf8mb4_general_ci 和 utf8mb4_bin 的区别
- utf8mb4_unicode_ci: 基于Unicode排序,支持所有语言,但速度相对慢
- 其比较逻辑更贴近人类对文字的理解: 忽略大小写,提升查询灵活性; 忽略部分重音符号,适配多语言场景(如会将 é 与 e、ñ 与 n 等视为等价)
- utf8mb4_general_ci: 没有实现 Unicode 排序规则,在遇到某些特殊语言或者字符集,排序结果可能不一致(在绝大多数情况下,这些特殊字符的顺序并不需要那么精确)。其他和 utf8mb4_unicode_ci 类似
- utf8mb4_bin: 如果需要存储大小写或重音符号敏感的数据,或加密数据或需要按二进制方式比较的场景,使用 utf8mb4_bin 排序规则。排序速度相对快,但对于部分不需要匹配大小写的场景需要通过lower转换影响性能
- utf8mb4_unicode_ci: 基于Unicode排序,支持所有语言,但速度相对慢
- 如果字段为
null判断问题- 判空需要使用
is null(不包含空字符串)或者is not null(包含空字符串) select * from t_test where username = 'smalle' and create_tm > '2000-01-01'直接使用 =、> 等字符比较,包含了此字段不为空的含义select * from t_test where (username is not null or username != '')这样判断才能确保username不为空白字符串(oracle的''和null相同,判断is not null即可)
- 判空需要使用
null排序问题- 字段排序时,null默认最小
select * from t_test order by username is null, username asc;此时先按照是否为null进行排序,是空的排在下面(返回1)
- 字段类型和大小
- varchar(10)表示可以显示10个字符,字符集utf8时一个中文为一个字符。mysql的utf8编码最大只能存放3个字节;utf8mb4中mb4指most bytes 4,因此最大可以存放4个字节。中文有可能占用2、3、4个字节
between...and左右边界都包含。当处理时间时(类型为datetime),语句between '2018-10-01' and '2018-11-01',实际执行between 2018-10-01 00:00:00 and 2018-11-01 00:00:00,从而少算了11-1的数据。解决办法- 写全时分秒,2018-10-01 00:00:00至2018-10-01 23:59:59
- 如果create_time类型为date(日期类型,而不是日期时间),则使用between…and没什么问题
date_format(a.create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') between '2018-10-01' and '2018-11-01'转成字符串进行比较between '2018-10-01' and date_add('2018-11-01', interval 1 day)多算了2018-11-02 00:00:00这一秒中的数据
关键字
常用函数
concat/concat_ws/group_concat
1 | -- 将多个字符串连接成一个字符串。任何一个值为null则整体为null |
instr/find_in_set
1 | -- instr (oracle也支持) |
日期
1 | -- sysdate |
with as
- 参考下文with-as用法
RECURSIVE CTE递归
- Mysql 8.0才支持此语法
1 | SELECT t.* FROM ( |
自定义变量
- 自定义变量的限制
- 无法使用查询缓存
- 不能在使用常量或者标识符的地方使用自定义变量,例如表名、列名或者limit子句
- 用户自定义变量的生命周期是在一个连接中有效,所以不能用它们来做连接间的通信
- 不能显式地声明自定义变量地类型
- mysql优化器在某些场景下可能会将这些变量优化掉,这可能导致代码不按预想地方式运行
- 赋值符号:=的优先级非常低,所以在使用赋值表达式的时候应该明确的使用括号
- 使用未定义变量不会产生任何语法错误
- 用户自定义变量只在session有效,退出后数据丢失
自定义变量的使用案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19-- 自定义变量的使用(@@为系统自定义变量)
set @one :=1;
select @one;
set @min_actor :=(select min(actor_id) from actor);
set @last_week :=(current_date-interval 1 week);
-- 在给一个变量赋值的同时使用这个变量
select actor_id,@rownum:=@rownum+1 as rownum from actor limit 10;
-- 避免重新查询刚刚更新的数据。eg:当需要高效的更新一条记录的时间戳,同时希望查询当前记录中存放的时间戳是什么
update t1 set lastUpdated=now() where id =1;
select lastUpdated from t1 where id =1;
-- 优化后:避免重新查询刚刚更新的数据
update t1 set lastupdated = now() where id = 1 and @now:=now();
select @now;
-- 注意where和select在查询的不同阶段执行
set @rownum:=0;
select actor_id,@rownum:=@rownum+1 as cnt from actor where @rownum<=1; -- 有问题的
select actor_id,@rownum as cnt from actor where (@rownum:=@rownum+1)<=1;
JSON数据类型
- 参考官网:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/json.html、https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/json-functions.html
- json_unquote 去掉了引号和转义符(和
->结合使用等同于->>) - json_extract 基于path提取json字段值(类似
->) - json_contains
- json_object 字符串转json对象
select json_object('a', 1, 'b', 'b1'); -- {"a": 1, "b": "b1"} - json_array 字符串转json数组
- json_table json转成临时表
- json_set 修改json
- json_unquote 去掉了引号和转义符(和
- 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhusf/p/15704599.html
1 | -- 创建数据类型为json的字段val(如果字段类型为字符串也是可以使用相关函数的,只不过存在隐式转换;且如果类型是json,则在插入数据时会进行格式校验) |
定时任务(事件)
- 可基于Navicat或者手动执行SQL创建任务
1 | -- 创建数据全局(mysql)定时任务日志表(可选) |
Oracle
常用函数
decode和case when
decode(被判断表达式, 值1, 转换成值01, 值2, 转换成值02, ..., 转换成默认值)只能判断=,不能判断like(like可考虑case when)select decode(length(ys.ycross_x), 1, '0' || ys.ycross_x, ys.ycross_x) from ycross_storage ys如果ys.ycross_x的长度为1那就在前面加0,否则取本身select sum(decode(shipcomp.company_num, 'CMA', 1, 0)) cma, sum(decode(shipcomp.company_num, 'MSK', 1, 0)) msk from ycross_in_out_regist yior ...(省略和shipcomp的关联)统计进出场记录中cma和msk的数量order by decode(col, 'b', 1, 'c', 2, 'a', 3, col)按值排序
case when then [when then ...] else end比decode强大case when t.name = 'admin' then 'admin' when t.name like 'admin%' then 'admin_user' else decode(t.role, 'admin', 'admin', 'admin_user') endsum(case when yior.plan_classification_code = 'Empty_Temporary_Fall_Into_Play' and yardparty.company_num = 'DW1' then 1 end) as count_dw1sum写在case里面则需要对相关字段(plan_classification_code)进行group by,而sum写外面则不需要对此字段group by. 主要用于分组之后根据条件分列显示
rollup
group by rollup分组统计grouping(col)判断某列是否为分组列,是则返回1否则返回0group_id()相同分组出现的次数,可以用于过滤重复数据grouping_id(col1, col2, ...)如grouping_id(a, b)小计返回1,总计返回3,其他返回0
1 | select |
- 结果
| A | B | C | D | SUM(N) | GID | ING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | C1 | D1 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | NULL | NULL | 5 | 0 | 1 |
| 小计 | 1 条 | NULL | NULL | 5 | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | C2 | D2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | NULL | NULL | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 小计 | 1 条 | NULL | NULL | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 总计 | 2 条 | NULL | NULL | 6 | 0 | 7 |
trunc时间处理
1 | select trunc(sysdate-1, 'dd'), trunc(sysdate, 'dd') from dual; -- 返回昨天和今天(2018-01-01, 2018-01-02) |
字符串处理
1 | -- length 获取字符长度; lengthb 基于字符获取长度 |
with-as用法
- 特点
- 特别是从多张表中取数据时,而且每张表的数据量又很大时,使用with写法可以先筛选出来一张数据量较少的表,避免全表join
- 可认为在真正进行查询之前预先构造了一个临时表,之后便可多次使用它做进一步的分析和处理。一次分析,多次使用
- mysql版本在8.0之前不能使用with的写法;8.0之后写法同oracle
- 语法(oracle/mysql均支持)
- 前面的with子句定义的查询在后面的with子句中可以使用,但是一个with子句内部不能嵌套with子句
- from后面必须直接紧跟使用with as出来的表,否则需要使用join将with as出来的表关联进来;在子查询中也是这样
- with必须开头,不能出现
select 1 from dual union all with ...
1 | -- 针对多个别名,e,d为“别名表” |
正则表达式
- 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/qmfsun/p/4467904.html
- 正则函数
regexp_like(匹配)比较一个字符串是否与正则表达式匹配(srcstr, pattern [, match_option])
regexp_instr(包含)在字符串中查找正则表达式,并且返回匹配的位置(srcstr, pattern [, position [, occurrence [, return_option [, match_option]]]])
regexp_substr(提取) 返回与正则表达式匹配的子字符串(srcstr, pattern [, position [, occurrence [, match_option]]])
regexp_replace(替换)搜索并且替换匹配的正则表达式(srcstr, pattern [, replacestr [, position [, occurrence [, match_option]]]])- srcstr: 被查找的字符数据
- pattern: 正则表达式
- position: 搜索在字符串中的开始位置。如果省略,则默认为1,这是字符串中的第一个位置
- occurrence: 它是模式字符串中的第n个匹配位置。如果省略,默认为1
- return_option: 默认值为0,返回该模式的起始位置;值为1则返回符合匹配条件的下一个字符的起始位置
- replacestr: 用来替换匹配模式的字符串
- match_option: 匹配方式选项。缺省为c
- c:case sensitive
- I:case insensitive
- n:(.)匹配任何字符(包括newline)
- m:字符串存在换行的时候被作为多行处理
1 | -- 分割函数:基于,分割,返回3行数据 |
案例
查找字表最新的一条记录
1 | -- 基于 keep |
查找中文
select * from t_customer t where asciistr(t.customer_name) like '%\%' and instr(t.customer_name, '\') <= 0;
一个字段存多个ID进行联表查询
1 | -- 也可将,进行分割后使用in进行联表查询,但是效率比此方法低很多 |
聚合函数(aggregate_function)
min、max、sum、avg、count、variance、stddevcount(*)、count(1)、count(id)、count(name)统计行数,不能统计值的个数。count(name),如果有3行,但是name有值的只有2行时结果仍然为3
wm_concat行转列
- 为oracle内部函数,12之后已经去掉了此函数
- 行转列,会把多行转成1行(默认用
,分割,select的其他字段需要是group by字段) - 案例
wm_concat(t.hobby)wm_concat(distinct t.hobby)支持去重select replace(to_char(wm_concat(name)), ',', '|') from test;替换分割符(默认为英文逗号)
自从oracle
11.2.0.3开始wm_concat返回的是LOB(CLOB)字段导致部分查询需要进行修改。参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wsxdev/p/15416946.html- 可使用to_char转换成varchar类型
- 虽然在wm_concat()函数外层包了一层to_char()函数,避免使用了LOB类型;但是由于wm_concat()函数的返回值类型LOB类型是不能进行group by、distinct以及union共存的,因此会偶发ORA-22922:错误。这里需要注意的是,是偶发,不是必然
也可在应用中处理clob直接返回到前台报错问题
可通过
clob.getSubString(1, (int) clob.length())解决1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12// JDBC
Object object = resultSet.getObject(i);
if(object != null) {
if(object instanceof java.sql.Clob) {
java.sql.Clob clob = (java.sql.Clob) object;
object = clob.getSubString(1, (int) clob.length());
}
}
// Mybatis处理
// https://juejin.cn/s/mybatis%20clob%20to%20string
// https://blog.csdn.net/lizhengyu891231/article/details/132434605或者使用jackson转换器,参考:https://oomake.com/question/13622930、https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000040484998
- 也可使用listagg within group行转列解决返回值为LOB的问题(但是长度最大为4000)
- 如果长度超过4000个字符,使用to_char会报错缓冲区不足,可以使用 xmlagg 函数代替(但不支持去重)。参考:https://www.cxybb.com/article/qq_28356739/88626952
- druid使用内置SQL解析工具类时,无法解析xmlagg函数,参考(测试无效):https://github.com/alibaba/druid/issues/4259
- 可使用to_char转换成varchar类型
xmlagg行转列
- 最大容量为4G,但是不支持去重
1 | -- 解决缓冲区问题:不使用to_char函数,在Java中需要用java.sql.Clob类,进行数据的接收与转换 |
listagg-within-group行转列
- listagg最大容量为4000
- mysql可使用group_concat
1 | -- 查询部门为20的员工列表 |
分析函数
常见分析函数
min、max、sum、avg一般和over/keep函数联合使用 ^3first_value(字段名)、last_value(字段名)和over函数联合使用row_number()、dense_rank()、rank():为每条记录产生一个从1开始至n的自然数,n的值可能小于等于记录的总数(基于相应order by字段的值来判断)。这3个函数的唯一区别在于当碰到相同数据时的排名策略。和over函数联合使用row_number当碰到相同数据时,排名按照记录集中记录的顺序依次递增(如:1-2-3-4-5-6)dense_rank当碰到相同数据时,此时所有相同数据的排名都是一样的(如:1-2-3-3-3-4. 如果被排序字段的值相等则认为排名相同)rank当碰到相同的数据时,此时所有相同数据的排名是一样的,同时会在最后一条相同记录和下一条不同记录的排名之间空出排名(如:1-2-3-3-3-6)
lag()、lead()求之前或之后的第N行。lag和lead函数可以在一次查询中取出同一字段的前n行的数据和后n行的值。这种操作可以使用对相同表的表连接来实现,不过使用lag和lead有更高的效率。和over函数联合使用- lag(列名, 偏移的offset, 超出记录窗口时的默认值)
rollup()、cube()排列组合分组。和group by联合使用group by rollup(a, b, c):首先会对(a、b、c)进行group by,然后再对(a、b)进行group by,其后再对(a)进行group by,最后对全表进行汇总操作group by cube(a, b, c): 首先会对(a、b、c)进行group by,然后依次是(a、b),(a、c),(a),(b、c),(b),(c),最后对全表进行汇总操作
connect by 递归关联
- mysql参考: RECURSIVE递归
start with connect by prior递归查询(如树形结构)
1 | select t.id, t.pid |
over
Mysql 8.0及以上也支持, 5.7不支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11-- 根据账号获取最新的用户访问ip
select t1.username,
(
select t2.ip
from t_user_ip t2
where t2.username = t1.username
order by t2.create_time desc
limit 1
) as ip
from t_user_ip t1
group by t1.username;分析函数和聚合函数的不同之处是什么:普通的聚合函数用group by分组,每个分组返回一个统计值,而分析函数采用partition by分组,并且每组每行都可以返回一个统计值 ^1
- 开窗函数只能在SELECT和ORDER BY中使用
开窗函数
over(),跟在分析函数之后,包含三个分析子句。形式如:over(partition by xxx order by yyy rows between aaa and bbb)^2- 子句类型
- 分组子句(partition by)
- 排序子句(order by)
- 窗口子句(rows):窗口子句包含rows、range和滑动窗口
- 窗口子句不能单独出现,必须有
order by子句时才能出现 - 取值说明
unbounded preceding第一行current row当前行unbounded following最后一行
- 窗口子句不能单独出现,必须有
- 省略分组字句:则把全部记录当成一个组
- 如果此时存在
order by,则窗口默认(省略窗口时)为当前组的第一行到当前行(unbounded preceding and current row) - 如果此时不存在
order by,则窗口默认为整个组(unbounded preceding and unbounded following)
- 如果此时存在
省略窗口字句
- 如果此时存在
order by,则窗口默认是当前组的第一行到当前行(不是整个组,是全量数据)- 出现
order by子句的时候,不一定要有窗口子句(窗口子句不能单独出现,必须有order by子句时才能出现)
- 出现
- 如果此时不存在
order by,则窗口默认是整个组 示例(示例和图片来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/linjiqin/archive/2012/04/05/2433633.html)
在线测试地址: https://livesql.oracle.com/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12-- 见图oracle-over-1: sql无排序, over排序子句省略
select deptno, empno, ename, sal, last_value(sal) over(partition by deptno) from emp;
-- (一般不推荐使用, 实际显示值和常规思路预期的不一致)
-- 见图oracle-over-2: sql无排序, over排序子句有, 窗口省略
select deptno, empno, ename, sal, last_value(sal) over(partition by deptno order by sal desc) from emp;
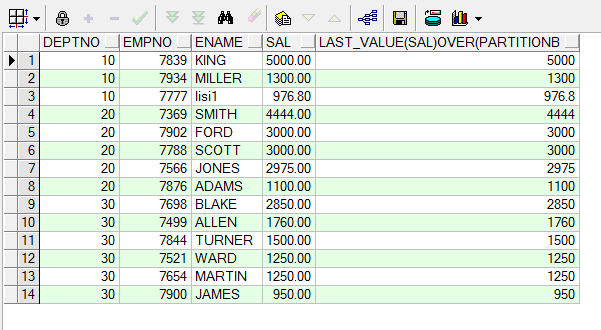
-- sql无排序, over()排序子句有, 窗口也有(窗口特意强调全组数据)
select deptno, empno, ename, sal,
last_value(sal) over(partition by deptno order by sal desc
rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) max_sal
from emp;oracle-over-1
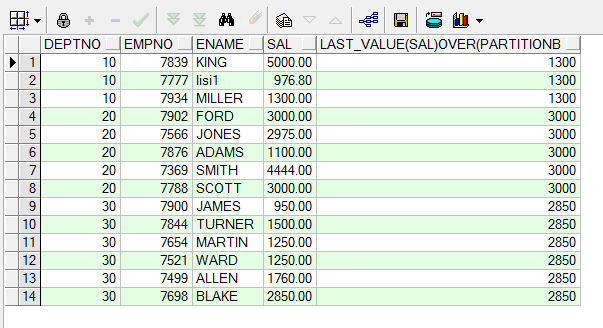
oracle-over-2
- 如果此时存在
两个
order by的执行时机- 两者一致:如果sql语句中的order by满足分析函数分析时要求的排序,那么sql语句中的排序将先执行,分析函数在分析时就不必再排序
- 两者不一致:如果sql语句中的order by不满足分析函数分析时要求的排序,那么sql语句中的排序将最后在分析函数分析结束后执行排序
- 子句类型
- 使用示例
1 | -- 查询有移动任务的场存,并获取每个场存需要移动的次数和最早一次移动计划的id |
over使用误区
主表行数并不会减少(普通的聚合函数用group by分组,每个分组返回一个统计值,而分析函数采用partition by分组,并且每组每行都可以返回一个统计值
查询每个客户每种拜访类型最近的一次拜访
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50-- ========= 原始数据
-- 原始拜访表数据(部分)
select v.id, v.visit_type, v.customer_id, v.comments, v.visit_tm
from t_visit v
where v.result is not null and v.valid_status = 1
and v.customer_id = 358330
order by v.visit_type, v.id desc;
-- 结果
#
1 93179 BS 358330 BS-3 2018/9/20
2 93165 BS 358330 BS-2 2018/9/21
3 93164 BS 358330 BS-1 2018/9/21
4 93252 IS 358330 IS-2 2018/10/8
5 27094 IS 358330 IS-1 2017/11/9
-- ========= 统计语句
-- *********错误sql一*********。(和group by混淆)
select
row_number() over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as rn
-- *********错误sql一*********
,first_value(v.id) over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as id -- 只取一个ID也是重复的
,first_value(v.customer_id) over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as customer_id
,first_value(v.visit_type) over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as visit_type
,first_value(v.comments) over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as comments
,first_value(v.visit_tm) over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as visit_tm
from t_visit v
where v.valid_status = 1 and v.result is not null
and v.customer_id = 358330;
-- 结果
# RN
1 1 93179 358330 BS BS-3 2018/9/20
2 2 93179 358330 BS BS-3 2018/9/20
3 3 93179 358330 BS BS-3 2018/9/20
4 1 93252 358330 IS IS-2 2018/10/8
5 2 93252 358330 IS IS-2 2018/10/8
-- *********错误sql二*********。此时报max(v.id)中的id不是group by字句(使用keep的话也会有这个错)
select
max(v.id) over(partition by v.customer_id, v.visit_type order by v.id desc) as id -- max(v.id):ORA-00979 not a group by expression
-- *********错误sql一*********
from t_visit v
where v.valid_status = 1 and v.result is not null
and v.customer_id = 358330
group by v.customer_id, v.visit_type
-- 可再次group by;或者使用row_number()再加子查询rn=1获取最大最小值
-- =============== 使用 Keep ===============
-- Keep测试一(基于主表group by)。参考下文[keep](#keep)
-- Keep测试二(基于over的partition by)。参考下文[keep](#keep)
keep
- keep的用法不同于通过over关键字指定的分析函数,可以用于这样一种场合下:取同一个分组下以某个字段排序后,对指定字段取最小或最大的那个值。从这个前提出发,我们可以看到其实这个目标通过一般的row_number分析函数也可以实现,即指定rn=1。但是,该函数无法实现同时获取最大和最小值。或者说用first_value和last_value,结合row_number实现,但是该种方式需要多次使用分析函数,而且还需要套一层SQL。于是出现了keep ^6
语法 ^5
1
2
3
4
5
6aggregate_function -- 聚合函数
KEEP (
DENSE_RANK { FIRST | LAST }
ORDER BY expr [ DESC | ASC ] [ NULLS { FIRST | LAST } ] [, expr [ DESC | ASC ] [ NULLS { FIRST | LAST } ]]...
)
[ OVER ( [query_partition_clause] ) ]- 最前是聚合函数,可以是min、max、avg、sum
dense_rank first,dense_rank last为keep函数的保留属性- dense_rank first 表示取分组-排序结果集中第一个(dense_rank值排第一的。可能有几行数据排序值一样,此时再可配合min/max等聚合函数取值)
- dense_rank last 同理,为最后一个
- Keep测试一(基于主表group by,如取最大最小值),场景参考上文over使用误区
1 | -- *****Keep测试一(基于主表group by)*****:如查分组中最新的数据(非分组字段通过keep获取,如果同最近的ID再次管理表则效率低一些) |
Keep测试二(基于over的partition by),场景参考上文over使用误区
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23-- 查询每个客户的默认地址:t_customer数据条数 28.9w, t_customer_address数据条数 36.8w。(注:此测试实际场景为两张表除了主键,无其他外键和索引)
select tmp_page.*, rownum row_id from ( -- 分页
select t.* from ( -- 写法 2(推荐)
select c.customer_name_cn
--,ca.address -- 写法 1
,max(ca.address) keep(dense_rank first order by decode(ca.address_type, 'Default', 1, 2)) over(partition by c.id) as address -- 写法 2
from t_customer c
left join t_customer_address ca on ca.valid_status = 1 and c.id = ca.customer_id -- 写法 2
/* -- 写法 1
-- 也曾尝试把子查询视图管理再主查询where之后(将主查询包裹一层再和此子查询关联),没有任何改观
left join (select ca.customer_id,
-- 需要根据客户地址类型排序,是导致子查询效率低的重要原因
max(ca.address) keep(dense_rank first order by decode(ca.address_type, 'Default', 1, 2)) as address
from t_customer_address ca
-- 写法1优化:通过查询主表(条件过滤之后会很少)在子查询内部过滤,主查询条件如果很多则所有的条件都需要写两遍,烦杂
--join t_customer c on c.id = ca.customer_id and c.valid_status = 1
where ca.valid_status = 1
group by ca.customer_id) ca
on ca.customer_id = c.id
*/
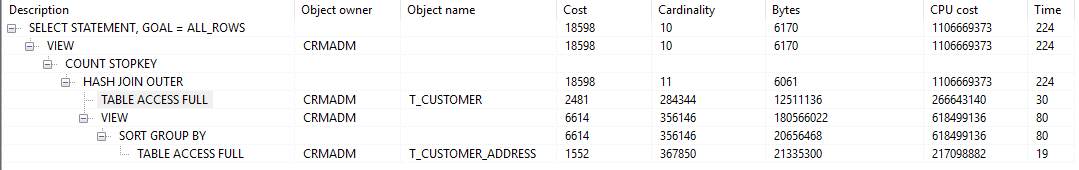
where c.valid_status = 1 -- and c.customer_name_cn = 'XXX有限公司' -- 只有一条此数据。加上次条件后写法1的分页需要 10s,写法2的分页只需 0.09s
) t group by t.customer_name_cn, t.address -- 写法 2(去重。此处必须套一层select去重。在里面加group by,语法层面ca.address、ca.address_type、ca.id都需要在group by字句中,则起不到去重效果)
) tmp_page where rownum <= 20 -- 分页写法 1
不使用分页执行计划。耗时 3.5s (PL/SQL自动分页显示20行)
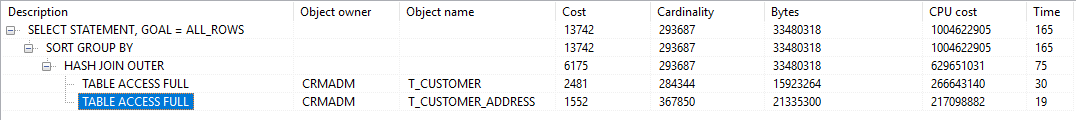
使用分页执行计划。耗时 4.2s (为什么分页导致效率变低???)
写法 2
不使用分页执行计划。耗时 0.8s (PL/SQL自动分页显示20行)
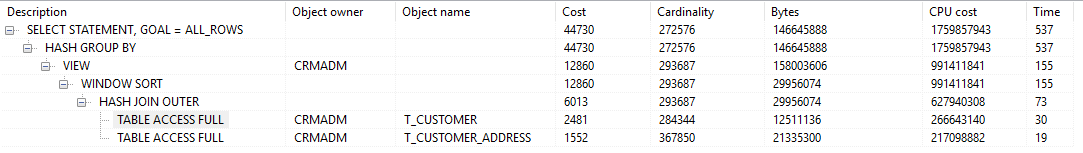
使用分页执行计划。耗时 0.7s
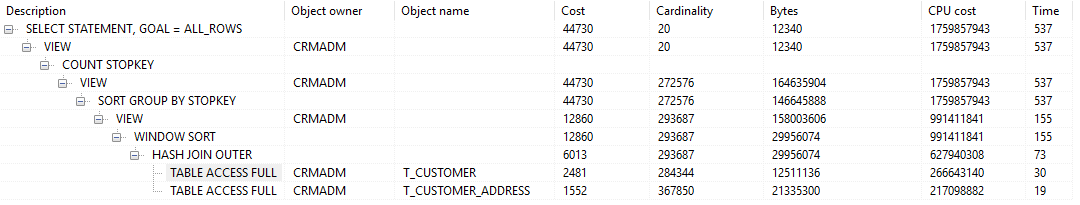
- 扩展测试
- 测试1:如上述sql注释,在主查询的where处加
and c.customer_name_cn = 'XXX有限公司',这样查询理论上只有一条此数据。加上次条件后写法1的分页需要 10s,写法2的分页只需 0.09s - 测试2:此时查询主表(t_customer)数据条数28.9w,曾测试查询主表只有2条数据(额外关联了几张较小的字段表)。写法1分页查询耗时 20s,写法2耗时 0.1s
- 测试1:如上述sql注释,在主查询的where处加
- 关于子查询 ^7
- 标准子查询:子查询先于主查询独立执行,返回明确结果供主查询使用。一般常见于where字句,且子查询返回一行/多上固定值(子查询中未使用主查询字段)
- 相关子查询:子查询不能提前运行以得到明确结果。一般常见于select字句、where字句(子查询中使用了主查询字段,如常用的exists)
- 此案例写法1使用子查询,不管子查询写在何处都需要子查询先返回一个视图,再供主查询调用。从而在获取子查询时必须全表扫描并排序
- keep和over联用,即可以查询子表最值,关联子表导致数据重复仍需group by去重
rollup、cube、grouping 小计、合计
- 结合group by获取小计、合计值
https://www.cnblogs.com/mumulin99/p/9837522.html
自定义函数
解析json
- 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/cyzshenzhen/article/details/17074543
select pkg_common.FUNC_PARSEJSON_BYKEY('{"name": "smalle", "age": "18"}', 'name') from dual;取不到age?
字符串分割函数
- 使用正则函数
1 | -- 基于,分割,返回3行数据 |
- (1)创建字符串数组类型:
create or replace type sq_type_arr_str is table of varchar2 (60);(一个数组,每个元素是varchar2 (60)) (2)创建自定义函数
sq_split1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32create or replace function sq_split(p_str in varchar2,
p_delimiter in varchar2)
return sq_type_arr_str
pipelined is
j int := 0;
i int := 1;
len int := 0;
len1 int := 0;
str varchar2(4000);
begin
len := length(p_str);
len1 := length(p_delimiter);
while j < len loop
j := instr(p_str, p_delimiter, i);
if j = 0 then
j := len;
str := substr(p_str, i);
pipe row(str);
if i >= len then
exit;
end if;
else
str := substr(p_str, i, j - i);
i := j + len1;
pipe row(str);
end if;
end loop;
return;
end sq_split;查询示例:
select * from table (cast (sq_split ('aa,,bb,cc,,', ',') as sq_type_arr_str));(一定要加as sq_type_arr_str) 结果如下:1
2
3
4
5
6COLUMN_VALUE
1 aa
2
3 bb
4 cc
5示例二
1
2
3
4
5select t.*
from test_table t
where exists (select 1
from table(cast(sq_split(t.name, ',') as sq_type_arr_str)) arr
where trim(arr.column_value) = 'aa')
Oracle中DBlink实现跨实例查询
- 同示例,跨用户可使用别名进行访问
1 | -- 创建DBLINK |
Oracle定时任务Job
- 说明
- jobs是oracle数据库的对象,dbms_jobs是jobs对象的一个实例,类比emp表是tables的实例
- 创建方式有差异,Job是通过调用dbms_scheduler.create_job包创建的,dbms_job则是通过调用dbms_job.submit包创建的
- oracle10g以后就推荐采用dbms_scheduler包来取代dbms_job来创建定时任务
- 任务可手动运行,无法自动运行任务
- 确保有可用的任务队列
select value from v$parameter where name like '%job_queue_processes%',如果任务队列太小或为0可通过此语句设置alter system set job_queue_processes =100; - 排查参考: https://www.modb.pro/db/394410
- 确保有可用的任务队列
- dbms_scheduler使用
1 | -- 创建任务 |
- dbms_scheduler执行频率repeat_interval支持两种格式
1 | -- repeat_interval 支持两种格式 |
- dbms_job使用
1 | -- 查询 |
- dbms_job执行频率举例
- 每天午夜12点
interval => 'trunc(sysdate + 1)' - 每天早上8点30分
interval => 'trunc(sysdate + 1) + (8*60+30)/(24*60)' - 每星期二中午12点
interval => 'next_day(trunc(sysdate), ''tuesday'') + 12/24' - 每个月第一天的午夜12点
interval => 'trunc(last_day(sysdate) + 1)' - 每个季度最后一天的晚上11点
interval => 'trunc(add_months(sysdate + 2/24, 3), ''q'') -1/24' - 每星期六和日早上6点10分
interval => 'trunc(least(next_day(sysdate, ''saturday''), next_day(sysdate, ''sunday''))) + (6×60+10)/(24×60)' - 每30秒执行次
interval => 'sysdate + 30/(24 * 60 * 60)' - 每10分钟执行
interval => 'trunc(sysdate, ''mi'') + 10/(24*60)' - 每天的凌晨1点执行
interval => 'trunc(sysdate) + 1 + 1/(24)' - 每周一凌晨1点执行
interval => 'trunc(next_day(sysdate, ''星期一''))+1/24' - 每月1日凌晨1点执行
interval => 'trunc(last_day(sysdate))+1+1/24' - 每季度的第一天凌晨1点执行
interval => 'trunc(add_months(sysdate, 3), ''q'') + 1/24' - 每半年定时执行(7.1和1.1)
interval => 'add_months(trunc(sysdate, ''yyyy''),6)+1/24' - 每年定时执行
interval => 'add_months(trunc(sysdate, ''yyyy''), 12)+1/24'
- 每天午夜12点
其他
1 | -- 去除换行chr(10), 去掉回车chr(13), 去掉空格。idea从excel复制数据新增时可能会出现换行 |
SqlServer
字符串处理
1 | -- STUFF(ori_str, start, length, add_str): 将ori_str从start位置删除length个字符,然后将add_str拼接在后面 |
with和表变量
1 | -- 方式一 |
语法树解析
- Druid
- 其组件SQL-Parser可进行SQL解析
- Apache Calcite
- 只支持通用的文法树,无法对不同数据库提供本地化支持
- antlr
- Antlr4是一个Java实现的开源项目,用户需要编写g4后缀的语法文件(有通用文件提供),Antlr4可以自动生成词法解析器和语法解析器,提供给开发者的接口是已经解析好的抽象语法树以及易于访问的Listener和Visitor基类。支持结构性语法,SQL解析只是其中一个应用场景
- 参考文章
参考文章
