RabbitMQ 简介
- RabbitMQ 的官方站:http://www.rabbitmq.com/
- 相关文章
- rabbitMQ 是一个在 AMQP 协议(高级消息队列协议)标准基础上完整的,可服用的企业消息系统。他遵循 Mozilla Public License 开源协议。采用 Erlang 实现的工业级的消息队列(MQ)服务器。
- 相关概念
Broker消息队列服务器实体VirtualHost在 RabbitMQ 中可以虚拟消息服务器 VirtualHost,每个 VirtualHost 相当于一个相对独立的 RabbitMQ 服务器,每个 VirtualHost 之间是相互隔离的,一个 broker 里可以开设多个 vhost,用作不同用户的权限分离。exchange、queue、message 不能互通。VirtualName 一般以/开头Exchange消息交换机,它指定消息按什么规则,路由到哪个队列Queue消息队列载体,每个消息都会被投入到一个或多个队列Binding绑定,它的作用就是把 exchange 和 queue 按照路由规则绑定起来RoutingKey路由关键字,exchange 根据这个关键字进行消息投递Producer消息生产者,就是投递消息的程序Consumer消息消费者,就是接受消息的程序Channel消息通道,在客户端的每个连接里,可建立多个 channel,每个 channel 代表一个会话任务
数据传输
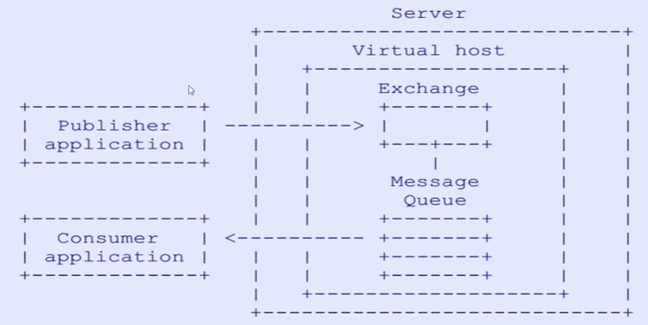
- 也可以不用先发送给交换机,直接点对点进行传输
- 生成者和消费者必须通过 Channel 向虚拟机开启一个会话
7 种消息模型:https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html
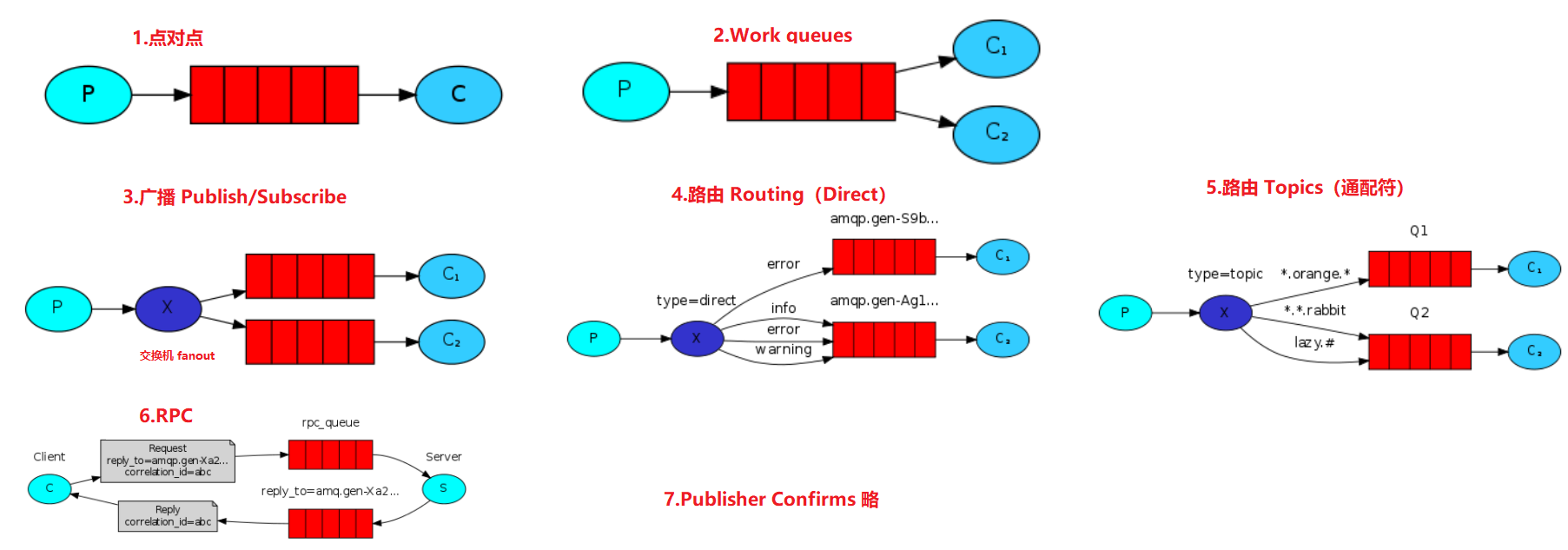
- 常用
- 点对点、工作队列(point和work模式配置相同,当多个消费者监听该队列时则任务是work模式,point只有一个消费者)
- 订阅类模式(包括:fanout 广播、direct 直连、topic 主题)
- 广播:同一消息,所有的消费者都可以接收到
- Direct 直连(RoutingKey 固定),只能接受固定类型的消息
- Topic 基于通配符(RoutingKey 包含通配符:*匹配一个单词,#匹配多个单词),只能接受主题相匹配的消息
- Publisher Confirms(发送确认模式):用来实现消息的可靠投递。当在某个通道(channel)上开启发布确认后,客户端发布的消息会被MQ服务器(broker)异步的确认 ^2
- 常用
相关原理
- RabbitMQ如何保证消息不丢失?
- 生产者发送消息不丢失
- 对于单个数据,生产者将消息发送到RabbitMQ,RabbitMQ将消息持久化到磁盘,并返回一个确认给生产者(支持同步确认和异步确认)
- 如果发送批量消息,可使用手动事务的方式保证消息正确发送:channel.txSelect() 开启事务;channel.txCommit()
提交事务;channel.txRollback() 回滚事务
- RabbitMQ消息存盘不丢消息
- 对于Classic经典队列,直接将队列声明成为持久化队列即可;Quorum队列和Stream队列都是默认持久化队列
- RabbitMQ主从消息同步时不丢消息
- 使用镜像模式集群,数据会主动在集群各个节点当中同步;另外,也可启用Federation联邦机制,给包含重要消息的队列建立一个远端备份
- RabbitMQ消费者不丢失消息
- RabbitMQ在消费消息时可以指定是自动应答,还是手动应答
- 如果是自动应答模式,消费者会在完成业务处理后自动进行应答,而如果消费者的业务逻辑抛出异常,RabbitMQ会将消息进行重试,这样是不会丢失消息的,但是有可能会造成消息一直重复消费(消费时考虑幂等即可)
- 在SpringBoot集成案例中,也可以在配置文件中通过属性
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode进行指定。可以设定为 AUTO 自动应答; MANUAL手动应答;NONE 不应答
- 生产者发送消息不丢失
- 如何保证消息幂等?
- 在SpringBoot集成案例中,可通过设置
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry开头的一系列属性,来制定重试策略,如重试此次等(未获取到应答时,RabbitMQ重复推送消息) - 在业务上需要给每个消息一个唯一的标识,从而再消费时进行判断
- 在SpringBoot集成案例中,可通过设置
- 如何保证消息的顺序?
- 可使用单队列+单消息推送,但是这种吞吐量会降低。目前RabbitMQ还没有比较好的解决方案,应该尽量避免
- RabbitMQ的数据堆积问题
- 新推出的Quorum队列以及Stream队列,目的就在于解决这个核心问题,但其生态不够完善,大部分企业还是基于Classic经典队列构建应用
- 应该尽量让消息的消费速度和生产速度保持一致,避免堆积产生
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.concurrency=5设置消费者的消费线程数量,spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.prefetch=1单次推送消息数量- 当确实遇到紧急状况,来不及调整消费者端时,可以紧急上线一个消费者组,专门用来将消息快速转录。保存到数据库或者Redis,然后再慢慢进行处理
RabbitMQ 安装
linux
1 | ## 安装erlang,版本有一定的要求,参考:https://www.rabbitmq.com/which-erlang.html。具体[参考下文](#erlang) |
windows
Rabbit MQ 是建立在强大的 Erlang OTP 平台上,因此安装 Rabbit MQ 的前提是安装 Erlang。通过下面两链接下载安装 3.7.7 版本
- 安装 Eralng OTP For Windows (opt21)
- 设置
ERLANG_HOME=D:\software\erl10.3 - 安装 RabbitMQ Server (3.8.7)
- 默认监听
5672端口(客户端连接使用此端口),开启后台则默认使用端口15672,默认超级管理员guest/guest
配置文件
- 参考:https://www.rabbitmq.com/configure.html#config-location
- 增加配置文件(可选):手动创建
$RABBITMQ_HOME/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf - 相关参数说明,配置文件样例
https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/blob/v3.7.x/docs/rabbitmq.conf.example
1 | # 默认为true,仅允许guest用户通过localhost访问;false表示任何网络均可访问 |
- 默认端口
5672客户端通信amqp端口15672开启后台则默认此http端口访问管理界面25672集群通信端口
相关命令
RabbitMQ 启动与停止
- windows
rabbitmq-service start启动 RabbitMQ 服务rabbitmq-service stop停止服务
- linux
rabbitmq-server -detached后台启动服务rabbitmqctl stop停止rabbitmqctl status
命令说明
1 | rabbitmq-server # **启动 RabbitMQ 和 Erlang VM**(关闭需要使用rabbitmqctl) |
rabbitmqctl
1 | ### rabbitmqctl |
rabbitmq-diagnostics
1 | # rabbitmq-diagnostics [--node <node>] [--timeout <timeout>] [--longnames] [--quiet] <command> [<command options>] |
简单使用
1 | # 添加用户和设置角色和权限 |
客户端使用
简单使用
- 相关代码参考 github-smjava-rabbitmq
- 引入客户端依赖
1 | <dependency> |
point/work(点对点/工作模式)
- point和work模式配置相同,当多个消费者监听该队列时则任务是work模式(point只有一个消费者)
1 | // =============== 生产者 |
topic
1 | // 获取连接(springboot则直接在配置文件中配置即可) |
整合 SpringBoot
- RabbitMQ 是实现了高级消息队列协议(AMQP)的开源消息代理软件,也称为面向消息的中间件。后续操作需要先安装 RabbitMQ 服务
- 引入对 amqp 协议支持依赖
1 | <dependency> |
- 配置 rabbitmq 服务器链接
1 | spring: |
- 配置队列、生产者、消费者
1 | // 配置队列 hello |
集群搭建
- 两种集群模式
- 普通集群模式
- 集群的各个节点之间只会有相同的元数据,即队列结构,而消息不会进行冗余,只存在一个节点中
- 消费时,如果消费的不是存有数据的节点, RabbitMQ会临时在节点之间进行数据传输,将消息从存有数据的节点传输到消费的节点
- 这种集群模式的消息可靠性不是很高
- 镜像集群搭建
- 是在普通集群模式基础上的一种增强方案,这也就是RabbitMQ的官方HA高可用方案,是基于普通集群增加镜像策略实现
- 其本质区别在于,这种模式会在镜像节点中间主动进行消息同步备份,而不是在客户端拉取消息时临时同步
- 并且在集群内部有一个算法会选举产生master和slave,当一个master挂了后,也会自动选出一个来
- 普通集群模式
- 高可用方案
- 使用Federation联邦插件给关键的RabbitMQ服务搭建一个备份服务
- 镜像集群+Haproxy+Keepalived
- 集群搭建(普通+镜像)
1 | ## 在 test1、test2、test3 三台机器上搭建rabbit服务 |
- 常见错误:
Authentication failed (rejected by the remote node), please check the Erlang cookie
1 | # 还有如下输出,此时 Erlang cookie hash 是.erlang.cookie文件内容经过hash得到,且.erlang.cookie文件处于/root目录。出现此问题可能是: |
插件
日志插件
- rabbitmq默认没有开启日志插件
- 开启插件
1 | # 开启插件 |
- 开启插件后还需手动设置,在后台管理界面 - Admin - Tracing可查看
- Add a new trace增加一个日志规则,假设Name=test,Format=Text,则会生成一个test.log的文件
- 在后台管理界面也可查看
- 日志格式
1 | ## 发送消息为"my-msg" |
后台管理
- 参考
- 常用测试配置
- 创建虚拟机(可省略,即使用默认的/):Admin-VirtualHost. 如需要多环境测试可创建虚拟机(因为队列必须一致,最简单的就是改变服务器/虚拟机配置)
- 创建项目用户:Admin-Users
- 创建项目队列(也可通过程序自动创建)
- 创建交换机(当使用订阅类模式时需要)
- 激活 Rabbit MQ’s Management Plugin(可激活管理插件)
- CMD 进入 RabbitMQ 安装目录,进入到 rabbitmq_server-3.8.7/sbin 目录
- 运行
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
- 登录管理后台
http://localhost:15672使用guest/guest登录(需要激活 rabbitmq_management)- 如果需要通过内网访问,可设置配置 loopback_users.guest=false,具体参考上文安装
- Overview 概览页面
Queued messages last minute最后一分钟所有队列中的消息- Ready 没有投递给消费者的消息(大于0则表示有消息堆积)
- Unacked 投递给消费者但是还没有收到ACK应答的(由于界面是数据是5s中刷新一次,如果消息较多此处可能有一定量的消息是此状态)
Message rates last minute最后一分钟所有队列的消费情况- Publish:producter pub消息的速率
- Publisher confirm:broker确认pub消息的速率
- Deliver(manual ack):customer手动确认的速率
- Deliver(auto ack):customer自动确认的速率
- Consumer ack:customer正在确认的速率
- Redelivered:正在传递’redelivered’标志集的消息的速率
- Get (manual ack):响应basic.get而要求确认的消息的传输速率
- Get (auto ack):响应于basic.get而发送不需要确认的消息的速率
- Return:将basic.return发送给producter的速率
- Disk read:queue从磁盘读取消息的速率
- Disk write:queue从磁盘写入消息的速率
- Connections 连接客户端查看页
- Channels 客户端会话查看页
- 在客户端的每个连接里,可建立多个 channel,每个 channel 代表一个会话任务
- Springboot一个消费者可能会自动创建多个会话
- Exchanges 交换机管理页
- Queues 队列管理页面
- Purge - Purge Messages 清空队列(将队列里的消息全部丢弃掉),或者执行
rabbitmqctl purge_queue xxx_queue
- Purge - Purge Messages 清空队列(将队列里的消息全部丢弃掉),或者执行
- Admin 管理员操作页面
- Users 用户管理
- Add a user 添加用户
- 点击用户进入详情页面
- Permissions 可设置用户权限
- 选择 Virtual Host,其他为
.*表示拥有此虚拟机的所有权限(包括配置交换机、队列等)
- 选择 Virtual Host,其他为
- Topic permissions 可设置监听消息队列和订阅权限
- 选择 Virtual Host,需要看队列所属的虚拟机
- Exchange交换机类型:如direct(默认)、topic
- 其他为
.*表示对此虚拟机下的该交换机类型拥有所有权限
- Update this user
- Tags 角色
- admin(administrator):管理员角色,可以管理所有虚拟机资源
- management:只能管理某个虚拟机下的资源
- Tags 角色
- Permissions 可设置用户权限
- Virtual Hosts 虚拟主机管理
- Add a new virtual host 添加虚拟主机
- 输入名称如
/vhost_aezocn_test,命名上 abc 和 /abc 是不同的 - 需要先有对应的虚拟主机,客户端才能连接
- 输入名称如
- 点击某个虚拟主机进入到详情页面
- Permissions 和 Topic permissions 可设置用户权限,参考 Users 中的
- Add a new virtual host 添加虚拟主机
- Policies 策略管理
- Users 用户管理
erlang
1 | # 不能使用默认源,否则安装的是R16B03-1。如是centos8则配置为.../el/8/ |
- 命令
1 | # 进入erlang shell。表示版为 R16B03-1 (rabbitmq 3.8.7 至少需要版本 OTP 21.3,参考:https://www.rabbitmq.com/which-erlang.html) |
参考文章
